The solution of water scarcity in Mauritania: (Small scale off-grid renewable energy water desalination system)
Sustainable Integrated Development Ecosystem
The problem of water scarcity is a major obstacle to development in Mauritania, as more than 42% of Mauritania’s population (2015) does not have potable water, in addition to more than 60% of Mauritanians who depend on agriculture and livestock

image source : Mid Journey artificial intelligence image generator
The majority of Mauritanians who suffer from water shortage live in rural and remote villages, where the population density in Mauritania is about 5 people per square kilometer, with an area of more than one million square kilometers. Connecting all these villages to the water network would be costly, and therefore the proposed solution was Digging wells and exploiting groundwater, however, the fresh groundwater is constantly decreasing, and most of the wells have become salty and unfit for drinking, which prompted the population to leave their villages and migrate towards the cities.
In this article, we will discuss an integrated and independent development model that depends entirely on local resources, and it is an ecosystem, the cornerstone of which is the desalination unit of groundwater by solar or wind energy, which will provide drinking water for humans, livestock and agriculture, and will also provide water High salinity concentration, suitable for fish farming and planting types of vegetables and fodder, this ecosystem will enable the creation of sustainable development and provide clean drinking water + agricultural and pastoral production, creating self-sufficiency for the inhabitants of these villages.


image source : Mid Journey artificial intelligence image generator
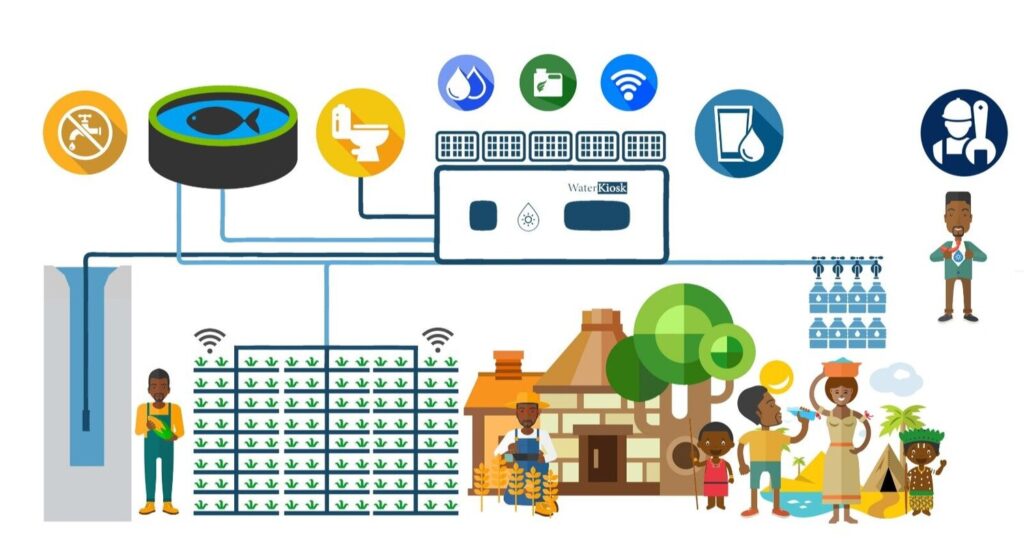
Source : https://www.winture.de/
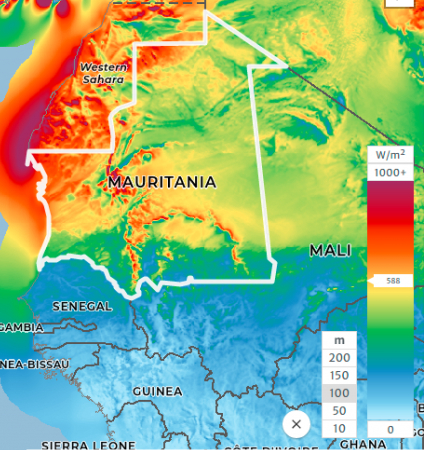
Mauritania has a high density of solar energy over the entire area of the country and also has strong wind energy, in addition to the presence of groundwater in abundance, which means that the basic elements are available, and the technology remains to exploit these resources as well. Great Leaps in Desalination Technology at Small Levels, Which Offers Efficient and Economical Solutions
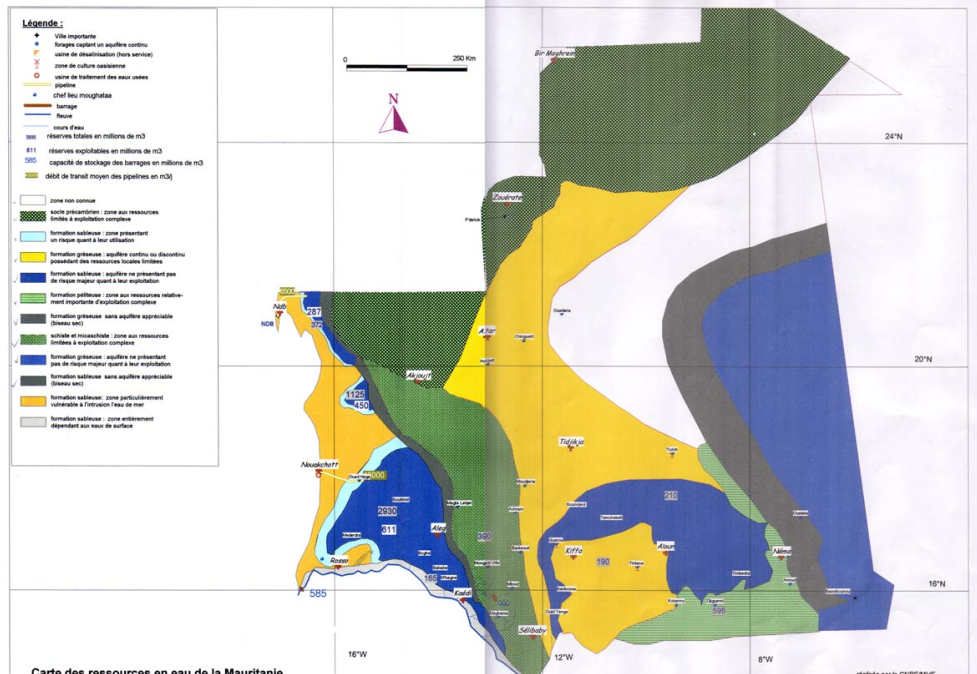
Water sources in Mauritania
Water resources are related to the geographical and rainfall characteristics of the. Figure shows the four principal resources in Mauritania
source :
Directory structure of OMRG/JICA mineral resource database
https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/11816725_08.pdf
Principal water resources are explained in Table
Table Principal Water Resources in Mauritania
| Colors on the Map | Characteristics for Resources |
| Yellow (Central Part) | Sandstone formation having a continuous or discontinuous water table with limited local reserve |
| Dark Blue (Four separated parts) | Sand formation water tables with adequate amount for their utilization. |
| Blue (Southeastern Part) | Sandstone formation water tables with adequate amount for its utilization |
| Light Gray (Around Senegal River) | Sand formation zone completely dependent on surface water |
Water resources over the Sahara and Sehel areas are limited, and the total amount of rainfall
in the Mauritania is small. There is a streamway in the Senegal River in the southeastern part of
Mauritania. Data on the potential water reserve whose validity was proved scientifically, is not
available, and the data on aquifer is both incomprehensive and limited. Therefore, it must be surveyed
scientifically.
The rain in areas with frequent rainfalls creates some water ponds with different lifetimes
depending on the local conditions like the intensity or frequency of the rainfalls. Heavy rainfall areas
5
are located to the north of Adrar, but the areas with most precipitation are located in the south and the
southeast between 15° and 18° in the latitude. From the viewpoint of water potential, these heavy
rainfall areas are the principal water sources. According to the World Union for Nature Conservation
(UICN), there are 250 to 320 places where it rains a lot in Mauritania. The principal surface water are
listed in Table 1.2. All of them are located in the southern Mauritania.
Table Principal Surface Waters in Mauritania
| Name | Brief explanation |
| Lake Aleg | Located near Aleg City (Brakna) with a maximum area of 5,000ha. |
| Lake Maal | Located southeast of Aleg City with a maximum area of 5,000ha. |
| Slough Tamourt en Naaj | Located in the Maritanide in Gorgol with an area of 1,600km2. |
| Lake R’kiz | Arable basin covered with water from Senegal River in Trarza. 5km (W),35km (L) |
| Slough Gouraya | Located south of Selibaby (Guidimaka). |
| Lake Foum Gleita | Artificial lake in Gorgol. |
| Slough Kankossa | Located in the Karakoro river basin (Assaba). |
Directory structure of OMRG/JICA mineral resource database
https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/11816725_08.pdf

image source : Mid Journey artificial intelligence image generator
Water Precipitation in Mauritania
WATER PRECIPITATION IN DEPTH
92 mm/year
Long-term average annual precipitation in depth (mm/year 2017)
WATER PRECIPITATION IN VOLUME
94.8 billion m³/year
(Long-term average annual precipitation in volume (billion m³/year 2017)
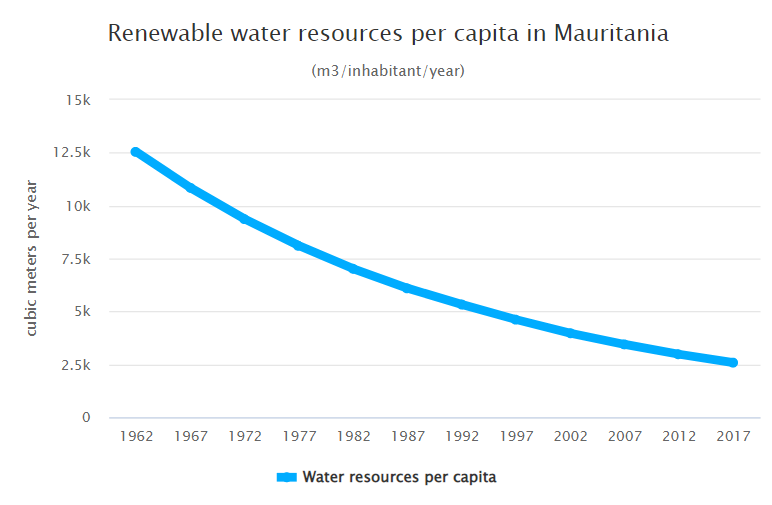
Water Resources in Mauritania
RENEWABLE WATER RESOURCES
11 billion m³/year
Total Renewable Water Resources (2017)
WATER RESOURCES PER CAPITA
2,579 m³/person/year
Renewable Water per Inhabitant (2017)
WATER DEPENDENCY
96 %
Water from outside the country (2017)
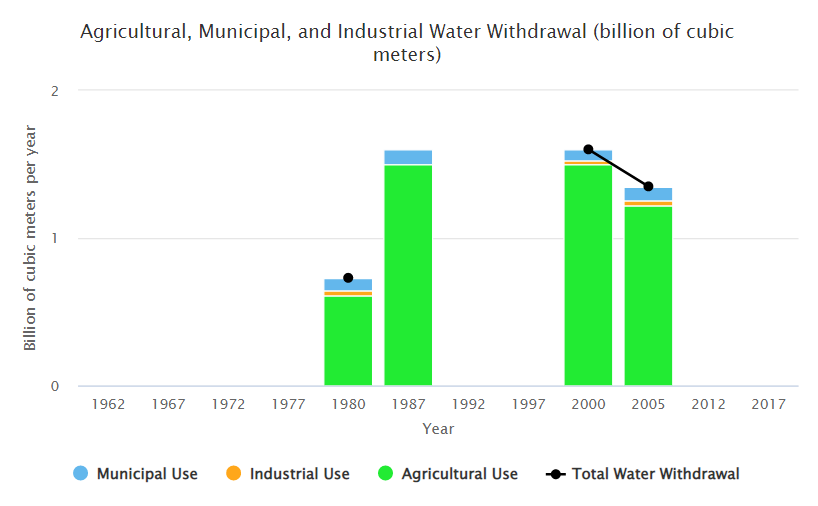
Water Use in Mauritania
Total, by Sector, and by Year
Notes: Years with missing data left empty.
Water use can include water used and then returned to its source (renewable resource).
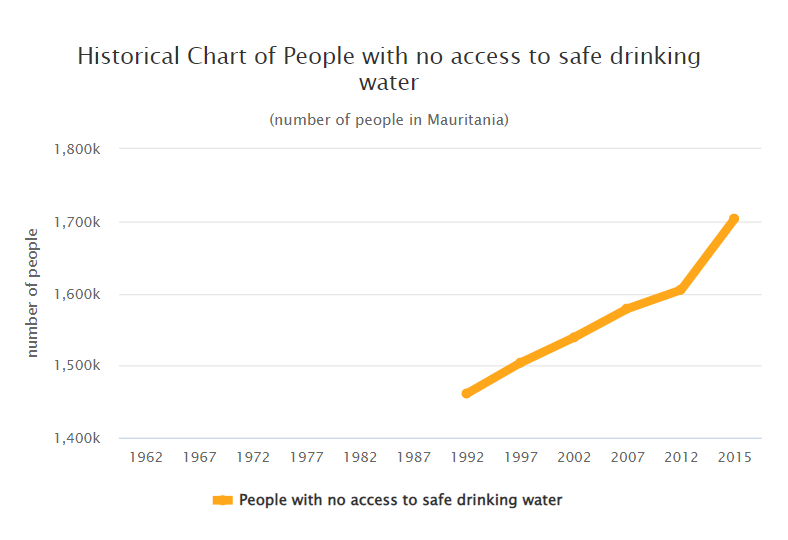
People with no access to a safe drinking water source in Mauritania
DON’T HAVE ACCESS TO SAFE DRINKING WATER
1,703,493 people
42.1 % of the population of Mauritania (2015)
The impact of climate change on population and water in Mauritania

image source : Mid Journey artificial intelligence image generator
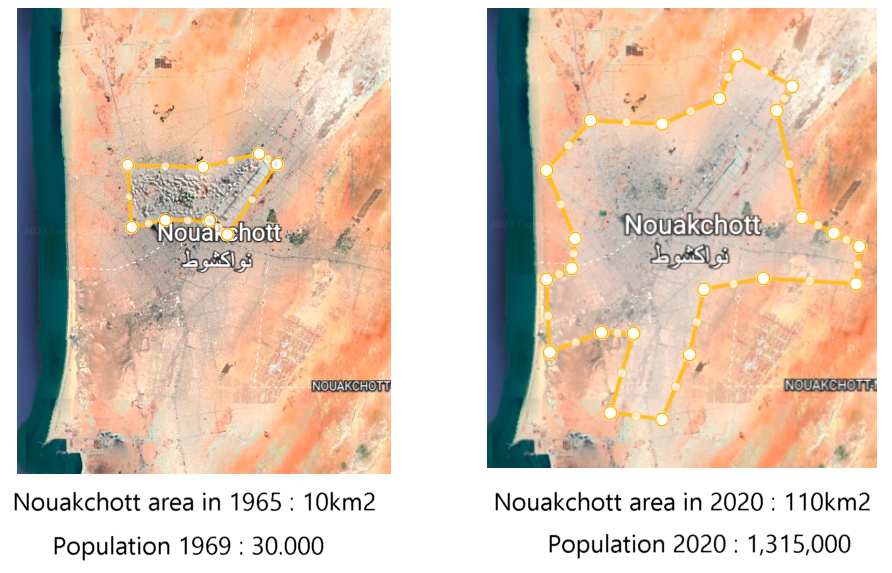
Mauritania was one of the country’s most affected by climate change and global warming, as droughts swept the country in the 70s of the twentieth century the majority of the population works in the field of agriculture and pastoral development
What, causing mass migrations from the countryside to major cities, especially Nouakchott, the capital, which was established at that time, which caused the horizontal expansion of the capital and the emergence of neighborhoods Randomness is what made the provision of infrastructure on this geographical scale, especially the water and sewage network
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XL4cLJJ6xh8https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kQj06z98pEc
More than any other locale, Nouakchott illustrated the problems brought about by rapid and uncontrolled urbanization. Originally a small administrative center, it had about 30,000 inhabitants in 1959 and more than 40,000 by 1970.
Because of the migrations from the countryside due to drought, it became The metro area population of Nouakchott in 2020 was 1,315,000, a 4.45% increase from 2019. The metro area population of Nouakchott in 2019 was 1,259,000, a 4.48% increase from 2018
Off-grid water solutions for rural development in Mauritania
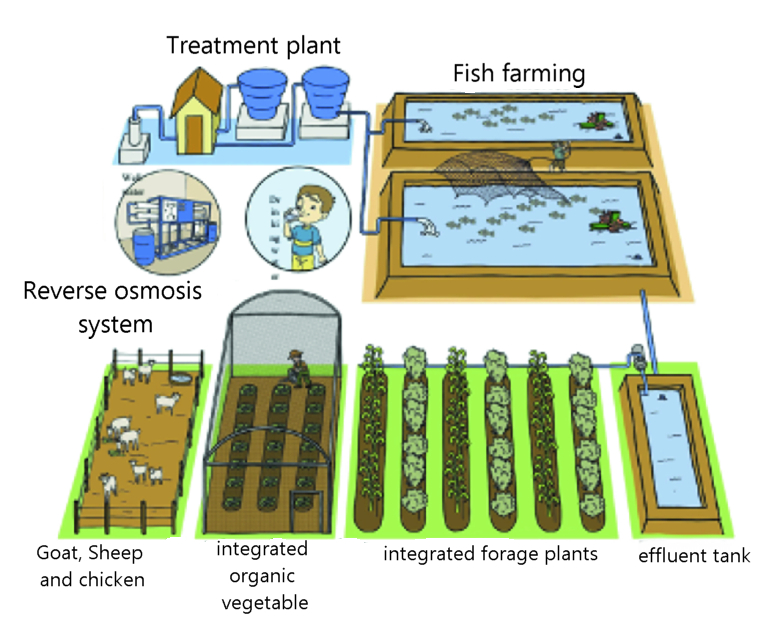
An integrated ecosystem that relies on local resources, and produces drinking water, vegetables, fish, small ruminants and poultry, fertilizers and organic fuels.
The elements of the system
The Energy : The system depends 100% on renewable energy, as Mauritania has great potentials from solar and wind energy, The solar panels or small wind turbine will supply the rest of the system with the energy needed to pump and desalinate water
Solar Energy Potential in Mauritania

Wind Energy Potential in Mauritania
Water : Groundwater is available in Mauritania, but most of it is salty water or contains heavy or polluted elements
Mauritania population density
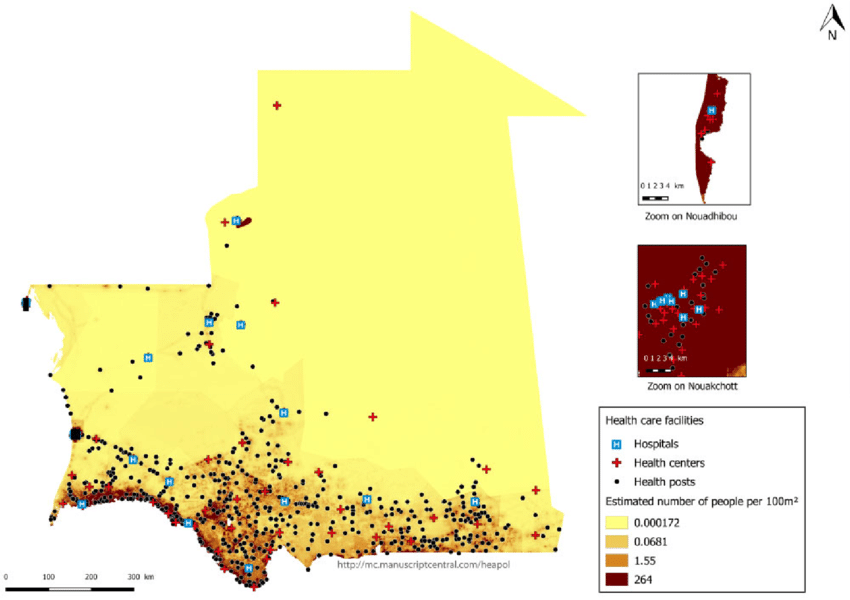
Mauritania groundwater map

Technology: Small-scale desalination systems powered by renewable energy, water pumps, irrigation and water storage systems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fcpDY9klZy0https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=26eyaXYIBuI
Sustainable Integrated Development Ecosystem
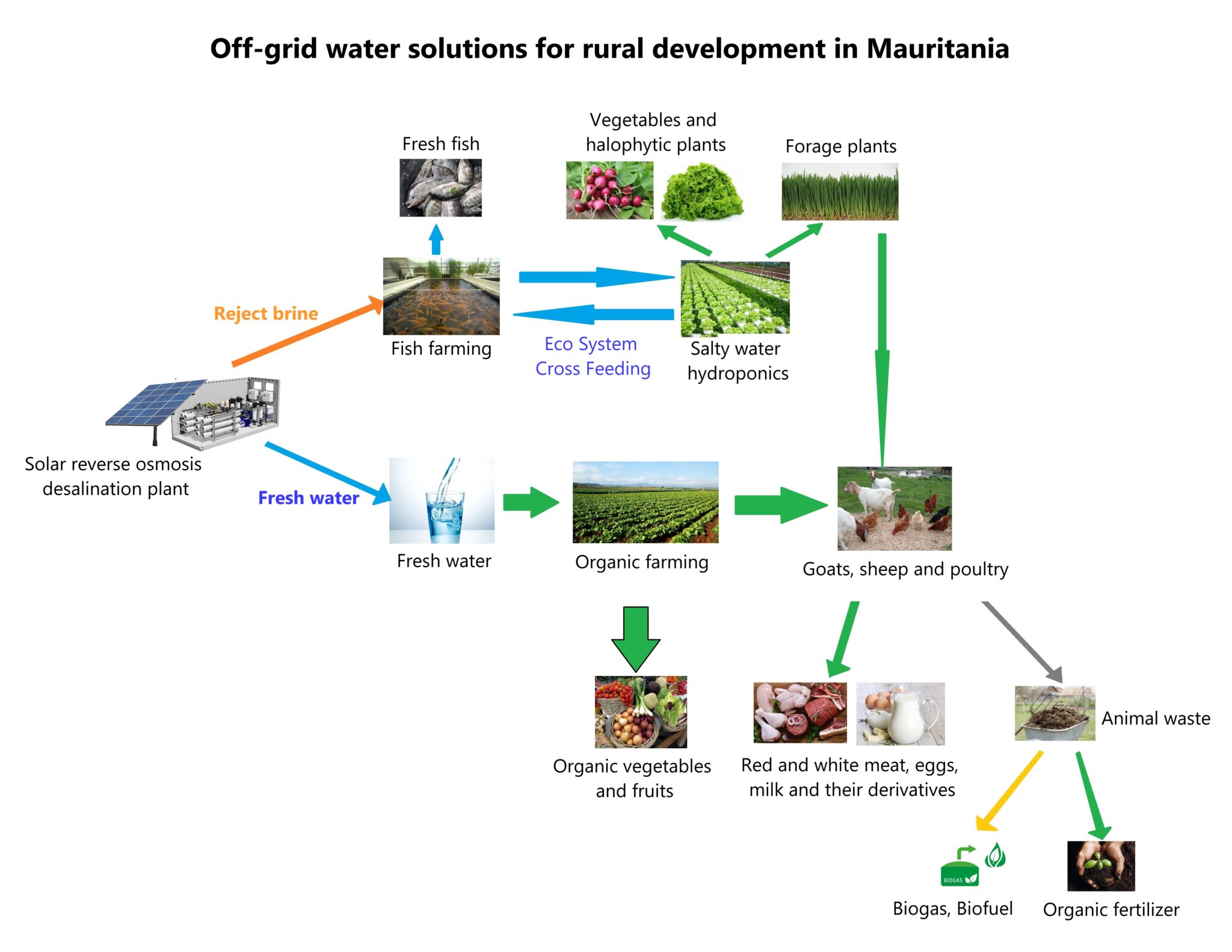
How it works
1- The reverse osmosis desalination system will produces potable water, and it also produces rejected brine water.
Fresh Water Path
1.1- Fresh water: Availability of safe drinking water is the basis of life and development. It will contribute to reducing water shortages in remote villages.
1.1.2- Organic farming: The availability of fresh water will contribute to the development of agriculture in remote villages, providing food, creating products and self-sufficiency for the inhabitants of these villages.
1.1.2.1- Production of organic vegetables and fruits.
1.1.3- The availability of water enhances pastoral production, especially sheep and goats, in addition to poultry, which will contribute to providing protein to the residents of remote villages and creating a sustainable source of income.
1.1.3.1- Production of red and white meat, eggs, milk and its derivatives.
1.1.3.2- Livestock produces animal waste that can produce fertilizers and biofuels.
1.1.3.2.1- Biofuels and biogas will be one of the most important high-value products, which will increase the productivity and added value of the project.
1.1.3.2.2- The organic fertilizer will contribute to improving the soil and increasing agricultural productivity, as it is an important product and an added value to the project.
Rejected Brine Path
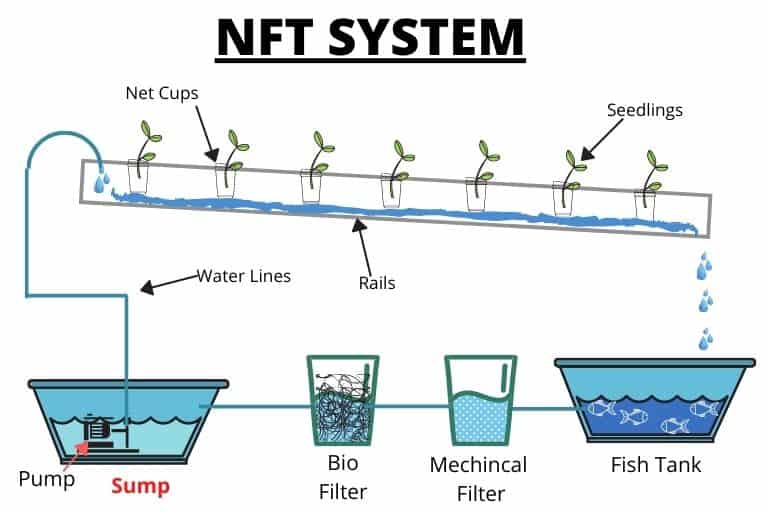
1.2- Instead of getting rid of the rejected brine, it can be used for fish farming and saline hydroponics to produce some vegetables and forage plants. This is the aquaponics system, which will contribute to increasing production in aquaculture and in fish farming, to be an integrated system.
1.2.1- Fish farming increases the benefit of villages from local resources and increases the proportion of bromine for each individual in the village
1.2.2- Saline hydroponics, in addition to producing vegetables and fodder plants, it’s also plays the role of a filter and reciprocal feeding between fish farming ponds and hydroponic ponds.
1.2.2.1- Produce vegetables that increase the agricultural products of the village.
1.2.2.2- The production of forage plants contributes to providing nutrition for livestock.
Project simulation “Off-grid water solutions for rural development in Mauritania”
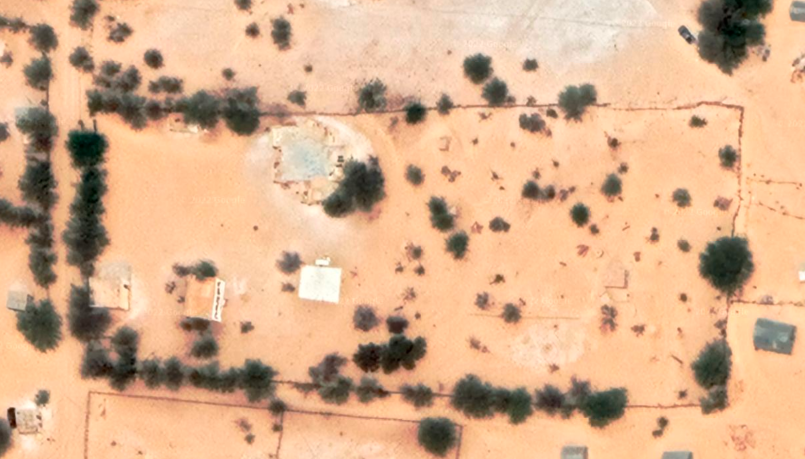
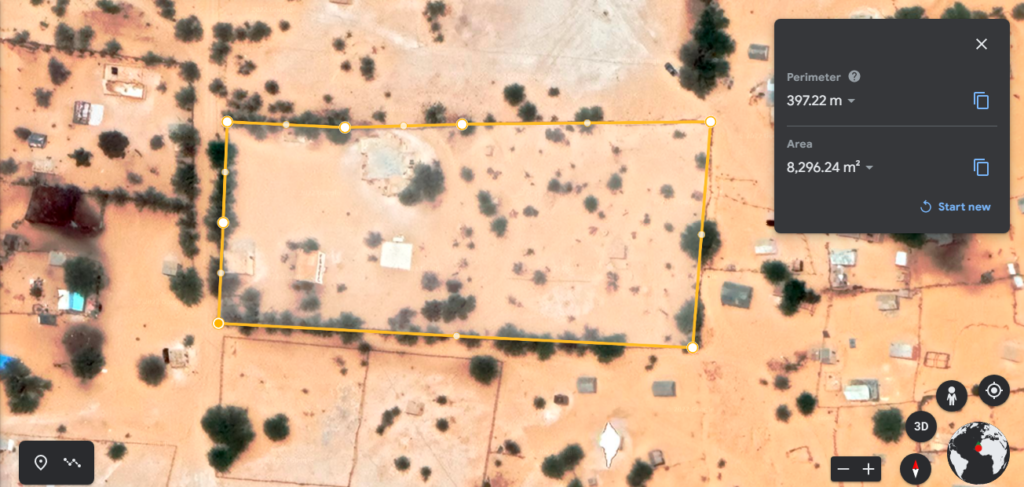


We have an (unused farm) east of the suburbs of Nouakchott on the “Al-Amal” road, with an area of 8250 square meters.
The farm is fenced and contains a well with a depth of 7 meters ( The water in the well is salty) and a cement tank of 12 cubic meters.
Equipment, tools and materials + expected time and costs
Step One
– Assessment of the condition of the well and cement tank, analysis of salinity and water components.
total cost of restoration the well and cement tank : 100$ – 1000$
total cost water analysis : 50$ – 100$

– Soil reclamation and preparation of the plots to be planted..
total cost : 200$ – 800$

– Construction of a sheep and goat barn with an area of 90 square meters
.
total cost : 200$ – 400$

– Construction of cement or plastic ponds for fish farming and hydroponics (Aquaponics System).
.
total cost : 500$ – 1000$


Estimated Time to Completion : 2 weeks – 5 weeks
Total cost : 1250$ – 3300$
Step Two
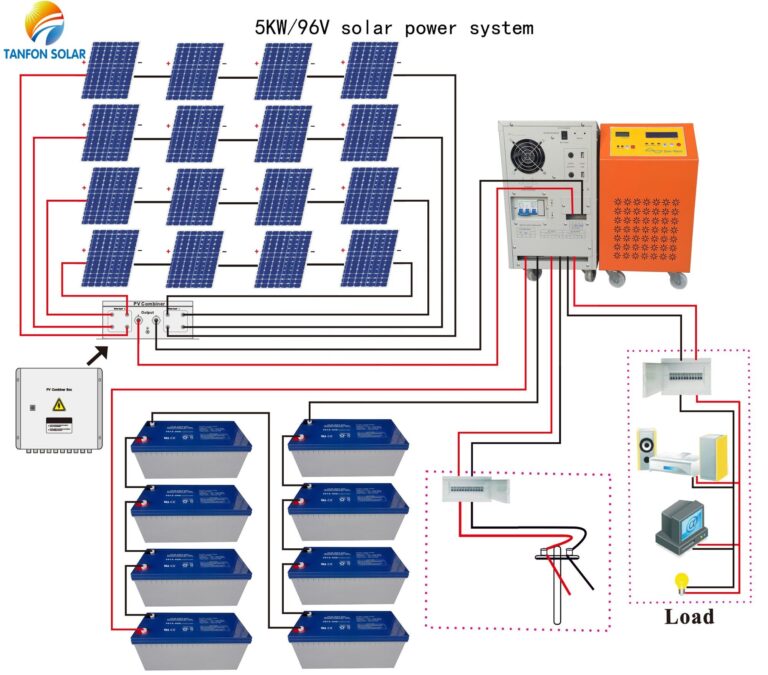
– Installing solar energy system 5kW , Used space = 30 m²
Total cost : 3000$ – 6000$
– Installing Water pumping system , Energy consumption = 1 kWh – 2kWh .
Total cost : 300$ – 700$
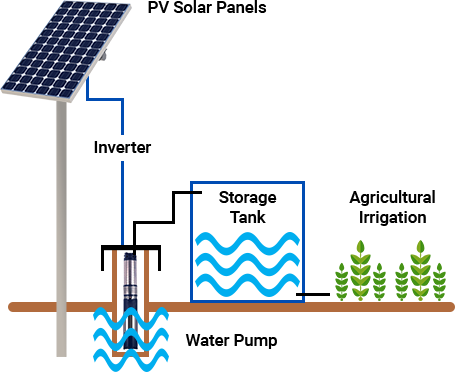
– Installing a water desalination (reverse osmosis system) with a production capacity of 15 cubic meters per day of fresh water and the same volume of brine water .Used space = 20 m² , Energy consumption = 2 kWh – 3 kWh per m3
Total cost : 7500$ – 12500$

– Aquaponics a system of aquaculture in which the waste produced by farmed fish or other aquatic animals supplies nutrients for plants grown hydroponically, which in turn purify the water. Used space = 30 m² , Energy consumption = 0.5 kWh -1 kWh.
Total cost : 1400$ – 2200$
– Drip Irrigation System Kits The most efficient irrigation method available is drip. Drip irrigation exceeds 90 percent efficiency, whereas sprinkler systems and hand watering are 50 to 70 percent efficient. Used space = 2000 m² ( frame area) , Energy consumption = 0.25 kWh – 0.70 kWh
Total cost : 300$ – 800$

Estimated Time to Completion : 4 weeks – 8 weeks
Total cost : 12,700$ – 22,800$
Step Three
– livestock, small ruminants such as goats and sheep, will have a role in purifying the project and increasing its revenues.
Total cost : 1000$ – 2000$ , Twenty heads of sheep and goats
– Fish larvae to be grown, in the aquaponics system
Total cost : 500$ – 1000$
– Seeds of vegetables, fruits and forage plants
Total cost : 200$ – 500$

Estimated Time to Completion : 1 weeks – 2 weeks
Total cost : 1700$ – 3500$
Total estimated Time to Completion :
7 weeks – 15 weeks
Total estimated budget :
15,000$ – 30,000$
Production Stage

After installing all the equipment and bringing the material, the project will start the work and production phase

Water Production

If the project is installed according to the previous plan, it will be able to produce 15 cubic meters of fresh water per day, or about 5,000 cubic meters annually.
In addition to the rejected salt water, which will be used in the aquaponic system
Fresh Water
15 cubic meters per day
5000 cubic meters per year
Rejected Brine
15 cubic meters per day
5000 cubic meters per year
Drip irrigation vegetable and fruit farm
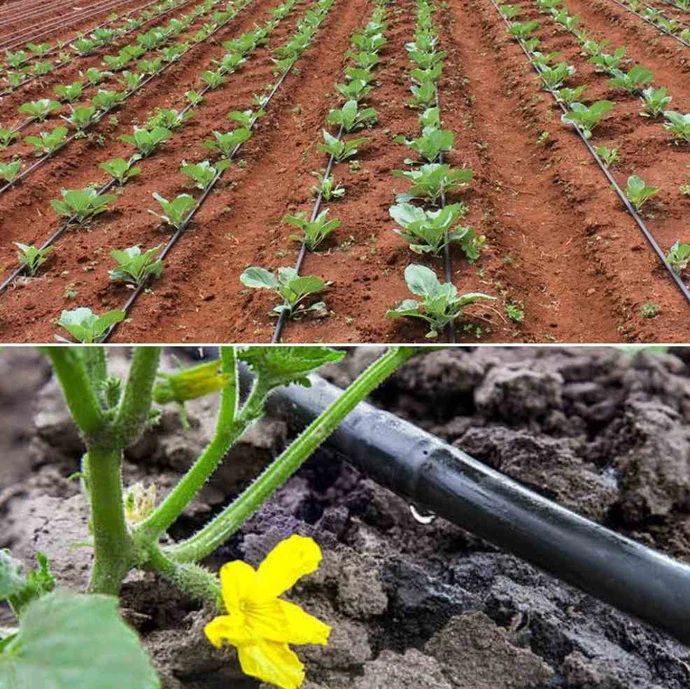

To save water and increase efficiency, we use the drip irrigation system, where we will be able to plant 2000 square meters with various vegetables and fruits, throughout the year the farm will be able to produce vegetables, fruits and fodder
Vegetables and Fruits productions
2 – 5 kg per Square Meter
The time taken to harvest the crop 60 to 120 days
Crop quantity 4000 – 10000 kg ( of fruits and vegetables every 4 months)
Aquaponics farms ( fish & vegetable )
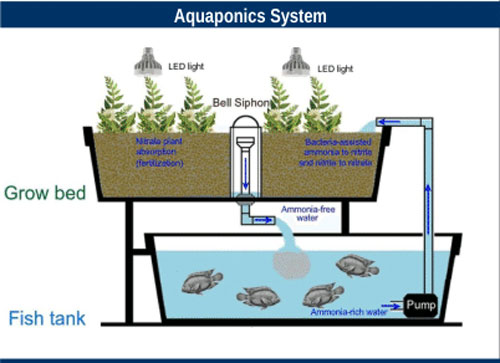
Aquaponics farms are extremely productive— yielding roughly 90000 kilograms of produce per acre, using at least 90% less water and land than dry-land farms, maturing products faster, and offering co-location with key distribution markets such as cities and export hubs.
An area of 30 square meters will be used for aquaponics
100 – 500 kg of Fish per year
1000 – 5000 kg of vegetable per year
Livestock (Goats, sheep and poultry) Production
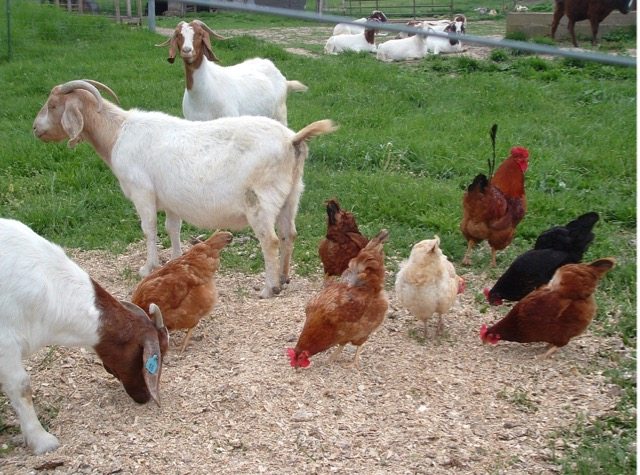

With the availability of water and fodder, the project provides a suitable environment for raising livestock, producing red and white meat, dairy and eggs, high quality products.
Sheep
10 heads of sheep
+20 heads of sheep every year
Goats
10 heads of Goats
+20 heads of goats every year
Poultry
starting with 30 heads of chicken
150 heads of chicken every 6 months
Documentation and publishing

